NECO BIOLOGY -OBJ
01-10: EEDDDEEAAE
11-20: DABBCACEBD
21-30: BCECCDADAD
31-40: DDBEBAEDBC
41-50: BACABABDDE
51-60: ACDCDCCDDA
=====
(1ai)
(i) Producers
(ii) Consumers
(iii) Decomposers
(1aii)
(i) Mandibles
(ii) Maxillae
(iii) Labium
(1bi)
(i) Filtration: Blood enters the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole and is filtered under pressure in the Bowman’s capsule, removing water, ions, glucose, amino acids, and waste products like urea from the blood.
(ii) Reabsorption: As the filtrate moves through the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct, essential substances such as water, glucose, and ions are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream.
(iii) Secretion: Additional waste products and excess ions are secreted into the tubule from the surrounding capillaries, ensuring the removal of substances not initially filtered or those that need to be regulated.
The final product, urine, collects in the renal pelvis, flows through the ureters to the bladder, and is excreted via the urethra.
(1bii)
(i) Malleus (Hammer)
(ii) Incus (Anvil)
(1biii)
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
-Converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using sunlight
-Only occurs in the presence of light (daytime)
RESPIRATION
-Converts glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water, and energy (ATP)
-Occurs continuously, day and night
===
(2ai)
(i) Wings
(ii) Hollow bones
(iii) Lightweight skeleton
(iv) Powerful muscles
(2aii)
-Pollen from anther (male part) is transferred to stigma (female part)
-Pollination occurs through agents like bees, butterflies, wind, or water
-Fertilization occurs when pollen germinates and sperm reaches the egg
-Seed formation and fruit development follow successful pollination
(2bi)
(i) Sticky tongue
(ii) Specialized teeth
(iii) Webbed feet
(2bii)
[TABULATE]
=ARTERIES=
(i) Carry blood away from the heart
(ii) No valves (except for the pulmonary artery and aorta)
(iii) Narrower lumen compared to veins
(iv) Thick, muscular, and elastic walls
=VEINS=
(i) Carry blood towards the heart
(ii) Valves present to prevent backflow of blood
(iii) Wider lumen compared to arteries
(iv) Thinner, less muscular, and less elastic walls
============================
(3ai)
(i) Phototropism
(ii) Geotropism
(iii) Hydrotropism
(iv) Thigmotropism
(3aii)
(i) Loss of fertile land and decreased agricultural productivity
(ii) Increased sedimentation in water bodies, harming aquatic ecosystems
(3bi)
Grass>Grasshopper>Lizard>Hawk
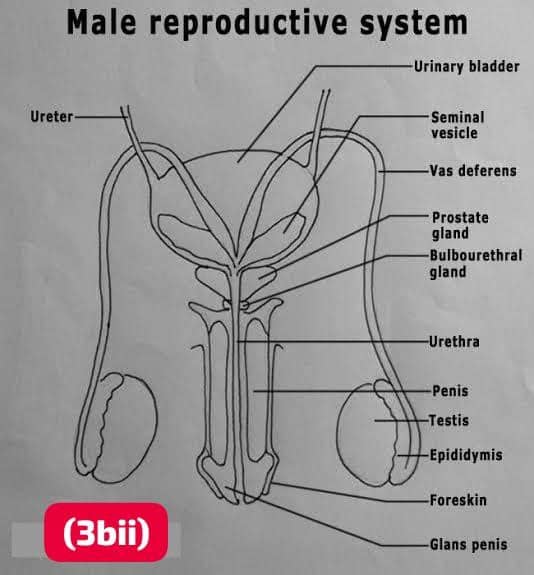
(3bii)
Diagram
(3biii)
(i) Oxygen (O₂)
(ii) Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
============================
(4ai)
(i) Humerus
(ii) Radius
(iii) Ulna
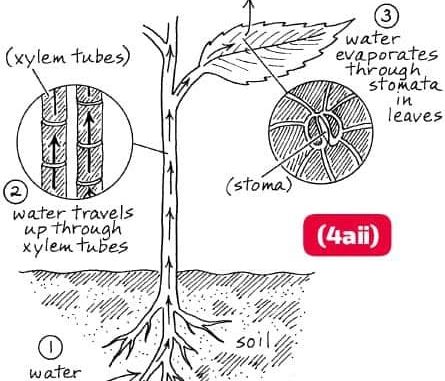
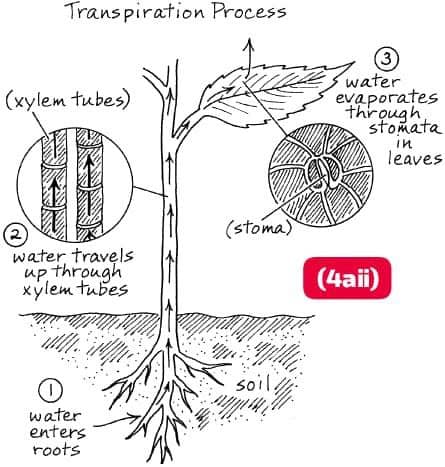
(4aii)
Diagram
(4bi)
(i) Insulin (regulates blood sugar levels)
(ii) Adrenaline (responds to stress)
(iii) Growth Hormone (regulates growth and development)
(4bii)
-Amoeba: Contractile vacuole
-Hydra: Diffusion through body surface
-Earthworm: Nephridia
-Grasshopper: Malpighian tubules
(4biii)
(1) Mitochondria: Generates energy for the cell through cellular respiration
(2) Lysosomes: Contains digestive enzymes to break down and recycle cellular waste and foreign substances
============================
(5a)
Diagram
(5bi)
[TABULATE]
=MONOCOT PLANTS=
(i) Leaf Venation; Parallel venation
(ii) Number of Flower Parts; Usually in multiples of three
=MONOCOT PLANTS=
(i) Leaf Venation; Reticulate (net-like) venation
(ii) Number of Flower Parts; Usually in multiples of four or five
(5bii)
(i) Fossil Record: Shows changes in species over time, with transitional forms demonstrating common ancestry.
(ii) Comparative Anatomy: Homologous structures (e.g., limb bones in vertebrates) indicate common ancestry.
(iii) Molecular Biology: DNA and protein sequence similarities among different species suggest evolutionary relationships.
(iv) Biogeography: Distribution of species across different geographical areas supports patterns of evolution and migration.
(5biii)
(i) Hinge Joint
(ii) Ball-and-Socket Joint
(iii) Pivot Joint
============================

Leave a Reply