*NECO 2024 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING ANSWERS*
`SECTION A: ANSWER TWO (2) QUESTIONS ONLY“`
(1a)
(i) Increased Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): If the cost to produce or acquire goods increases, it directly reduces the gross profit margin. Factors such as rising raw material costs, increased labor costs, or higher production expenses can contribute to this.
(ii) Competitive Pricing Pressure: When competitors lower prices or enter the market with lower-priced alternatives, a business may need to reduce its own prices to remain competitive. This can squeeze the gross profit margin unless offset by increased sales volume.
(iii) Declining Sales Volume: If a business experiences lower sales volumes, it may not generate enough revenue to cover fixed costs and maintain previous levels of profitability. This decline in revenue directly impacts the gross profit margin.
(1b)
(i) Cost of the asset
(ii) Useful life
(iii) Salvage value
(iv) Depreciation method
(v) Residual value
(1c)
(i) Wear and tear
(ii) Obsolescence
(iii) Accidental damage
===================================
(2)
(i) Proforma Invoice:
A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice sent by a seller to a buyer before the shipment of goods. It’s a quote or an estimate of the goods’ value, indicating the terms of sale, including price, quantity, and payment terms. It’s not a demand for payment but rather a declaration of the seller’s intention to supply the goods.
(ii) Goodwill:
Goodwill is an intangible asset that represents the value of a business’s reputation, customer relationships, and brand recognition. It’s the excess amount paid for a business over its net asset value. Goodwill is a non-current asset that appears on the balance sheet and is amortized over its useful life.
(iii) Consignee:
A consignee is the person or business to whom goods are shipped, but who does not own the goods until they are sold. The consignee acts as an agent for the owner of the goods (the consignor) and is responsible for storing, displaying, and selling the goods. The consignee receives a commission on the sale price, and the remaining amount is remitted to the consignor.
(iv) Preference Share:
Preference shares are a type of share that has a higher claim on assets and dividends than ordinary shares. Preference shareholders receive a fixed dividend payment before ordinary shareholders and have priority in receiving assets in case of liquidation. However, they usually don’t have voting rights.
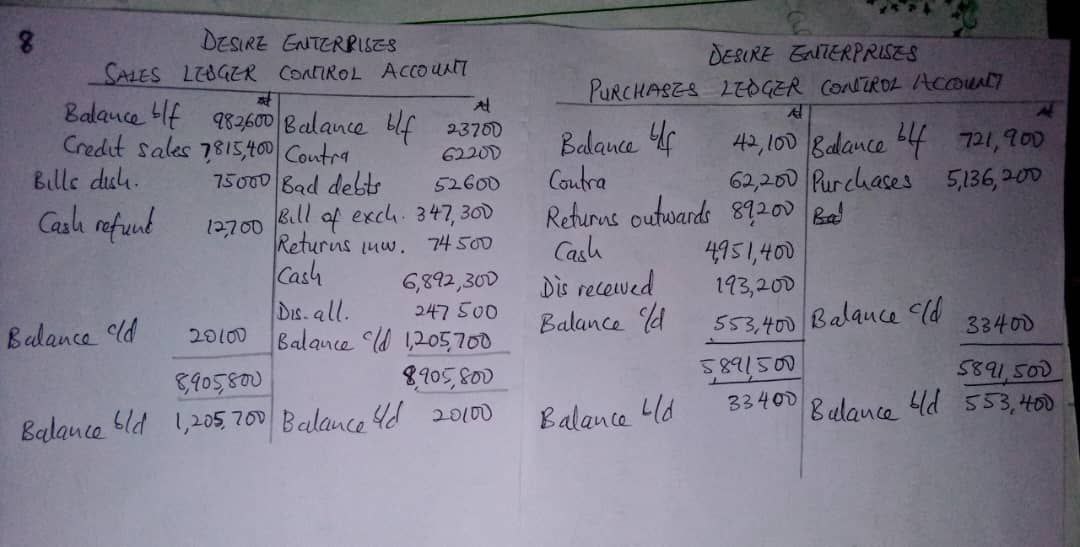
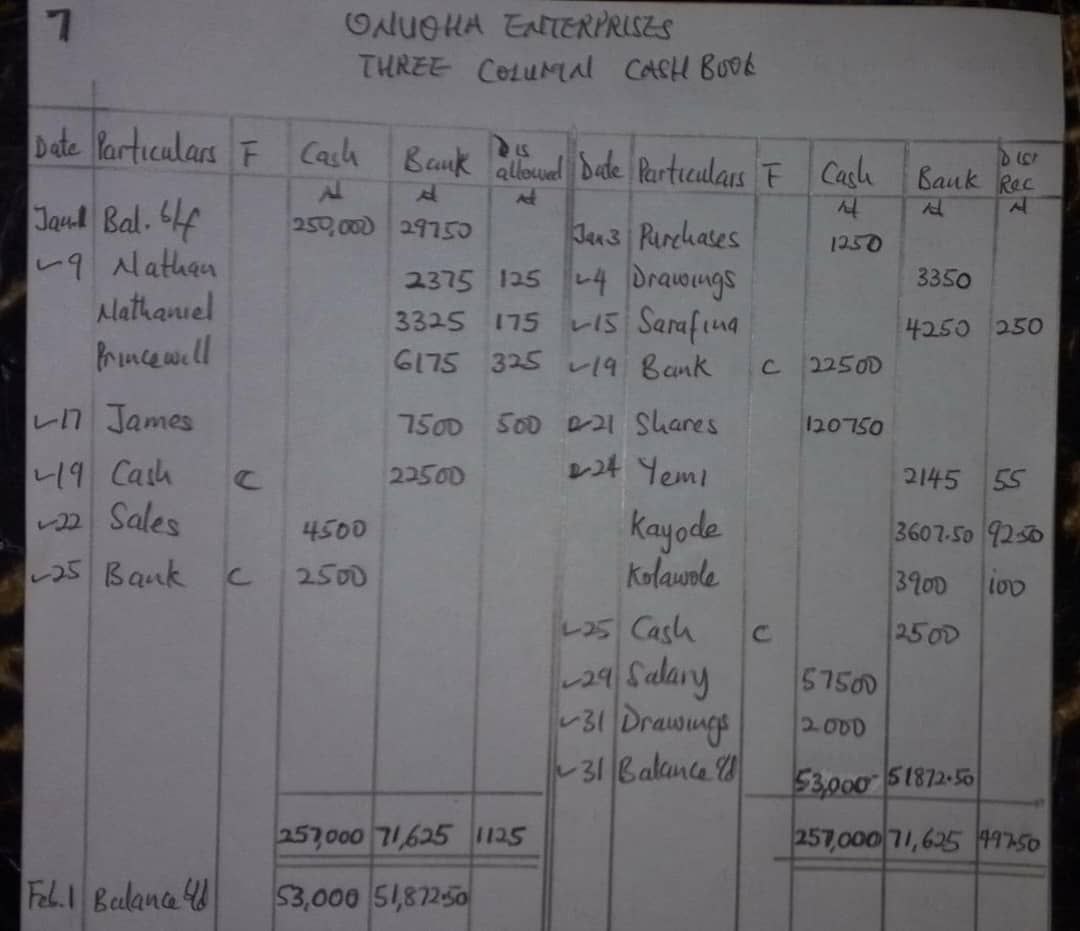
(v) Three Column Cash Book:
A three column cash book is a specialized accounting record that includes columns for cash transactions, bank transactions (such as cheques received and issued), and discounts allowed and received. It provides a structured way to record and reconcile cash and bank transactions in a single book, aiding in accurate financial management and reporting.
===================================
(3a)
(i) Compensating errors: These errors occur when two or more errors in different accounts cancel each other out, resulting in a correct total. For example, if a company accidentally records a $1,000 increase in both assets and liabilities, the trial balance will still be correct, but the financial statements will be inaccurate.
(ii) Errors of principle: These errors occur when a transaction is recorded in the wrong account category. For example, recording an expense as an asset or a revenue as an expense. This type of error will not be detected by the trial balance, but it will affect the financial statements.
(iii) Errors of omission: These errors occur when a transaction is not recorded at all. For example, if a company fails to record a sale or a purchase, the trial balance will still be correct, but the financial statements will be incomplete.
(iv) Entry in the wrong account: These errors occur when a transaction is recorded in a correct account but with the wrong amount. For example, recording a $100 sale as $1,000. This type of error will not be detected by the trial balance, but it will affect the financial statements.
(v) Error in the accounting equation: These errors occur when the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) is not maintained. For example, increasing assets without increasing liabilities or equity. This type of error will not be detected by the trial balance, but it will affect the financial statements.
(3b)
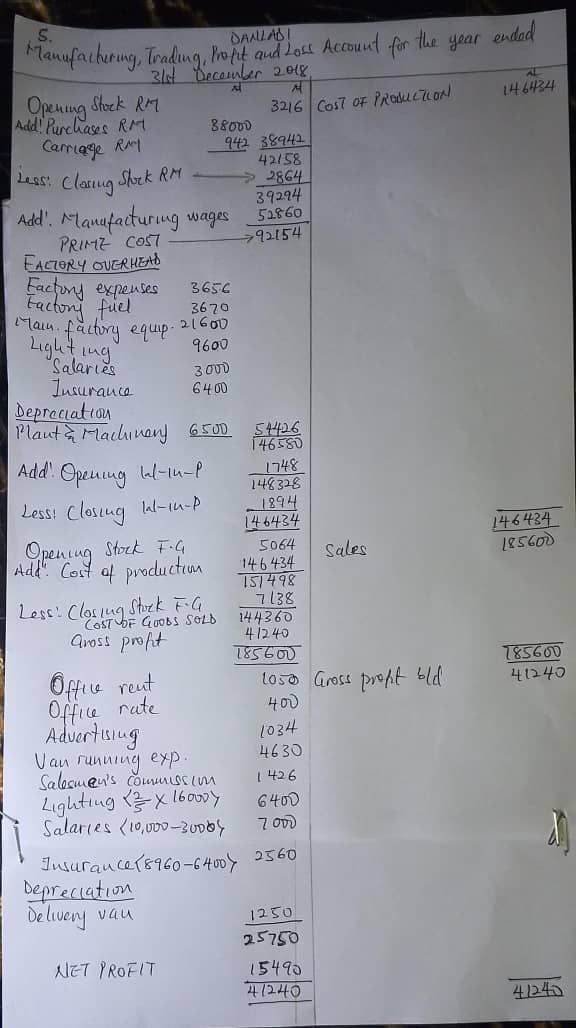
(i) Direct materials cost
(ii) Direct labour cost
(iii) Factory overheads
(iv) Depreciation
(v) Factory expenses
===================================
(4a)
[TABULATE]
Appropriation account of a Partnership:
(i) Appropriation account is used to distribute profits and losses among partners.
(ii) It shows the allocation of profits to partners’ capital accounts.
(iii) It’s a nominal account, not a permanent account.
Appropriation account of a Company:
(i) Appropriation account is used to distribute profits to shareholders as dividends.
(ii) It shows the allocation of profits to retained earnings or reserves.
(iii) It’s a permanent account, not a nominal account.
(4b)
(i) Liquidity: Working capital provides the necessary funds for daily operations.
(ii) Creditworthiness: Adequate working capital improves a company’s creditworthiness.
(iii) Growth: Working capital funds expansion and investment opportunities.
(iv) Risk management: Working capital helps absorb unexpected expenses or revenue shortfalls.
(v) Efficiency: Working capital enables businesses to take advantage of discounts and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
(4c)
(i) Recording non-routine transactions
(ii) Correcting errors
(iii) Adjusting entries
===================================


Leave a Reply